HTML
HTML, or Hypertext Markup Language, is the standard markup language used to create web pages. It provides a set of tags and attributes that are used to describe the structure and content of a web page. HTML is a fundamental building block for web development and is used in conjunction with other web technologies such as CSS and JavaScript. With HTML, you can create headings, paragraphs, lists, links, images, and much more. It is easy to learn and can be used to create basic websites or complex web applications.
Form and Validations
Forms
A form in HTML5 is declared with the tag <form> and consists of every element that is found before the closing tag </form>.
The <form> element is a container for different types of input elements, such as: text fields, checkboxes, radio buttons, submit buttons, etc.
To declare any of these inputs, we use the input element, <input>.
For the type of the input, we simple declare it inside the tag with the attribute type.
For example, <input type="text">.
Validations
Go to any popular site with a registration form, and you will notice that they provide feedback when you don’t enter your data in the format they are expecting. You’ll get messages such as:
- “This field is required” (You can’t leave this field blank).
- “Please enter your phone number in the format xxx-xxxx” (A specific data format is required for it to be considered valid).
- “Please enter a valid email address” (the data you entered is not in the right format).
- “Your password needs to be between 8 and 30 characters long and contain one uppercase letter, one symbol, and a number.” (A very specific data format is required for your data).
This is called form validation. When you enter data, the browser and/or the web server will check to see that the data is in the correct format and within the constraints set by the application. Validation done in the browser is called client-side validation, while validation done on the server is called server-side validation.
We want to
- get the right data, in the right format. Our applications won’t work properly if our users’ data is stored in the wrong format, is incorrect, or is omitted altogether.
- protect our users’ data. Forcing our users to enter secure passwords makes it easier to protect their account information.
- protect ourselves. There are many ways that malicious users can misuse unprotected forms to damage the application.
Different types of client-side validation:
- Built-in form validation uses HTML5 form validation features. This validation generally doesn’t require much JavaScript. Built-in form validation has better performance than JavaScript, but it is not as customizable as JavaScript validation.
- JavaScript validation is coded using JavaScript. This validation is completely customizable, but you need to create it all (or use a library).
Using built-in form validation attributes:
- required: Specifies whether a form field needs to be filled in before the form can be submitted.
- minlength and maxlength: Specifies the minimum and maximum length of strings.
- min and max: Specifies the minimum and maximum values of numerical input types.
- type: Specifies whether the data needs to be a number, an email address, or some other specific preset type.
- pattern: Specifies a regular expression that defines a pattern the entered data needs to follow.
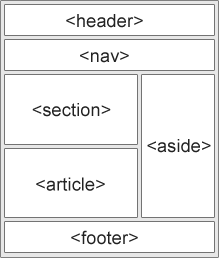
Semantic and non-semantic HTML
A Semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer.
- non-semantic elements:
<div>,<span> - semantic elements:
<article>,<footer>,<form>,<header>, etc
SEO
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing a website to improve its visibility and ranking on search engines like Google. By properly implementing SEO techniques in your HTML, you can improve the chances of your website ranking higher on search engine results pages, which can lead to more traffic and potential customers for your business.
Key Elements of HTML SEO
-
Page Title: The page title is the title that appears on the search engine results page. It should be descriptive and concise, and should accurately reflect the content of the page. It should also include primary keywords.
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here. -
Meta Description: The meta description is a brief summary of the page content that appears below the page title on the search engine results page. It should be concise and compelling, and should include primary keywords.
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here. -
Headings: Headings, or “H” tags, are used to structure the content on a page and make it easier for search engines to understand the hierarchy of the information. Properly using headings can also help improve the visibility of your page on search engine results pages.
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here. -
Alt Text: Alt text, or “alternative text”, is used to describe images on a page. It is important to include alt text for images, as search engines cannot see images and rely on the alt text to understand the content of the image.
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here. -
URLs: URLs, or “uniform resource locators”, are the web addresses of pages on your site. URLs should be descriptive and include primary keywords.
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here.
Tips for Improving HTML SEO
- Use keyword-rich page titles, meta descriptions, and URLs.
- Use headings to structure the content on your page and include keywords in your headings.
- Use alt text to describe images on your page.
- Use external and internal links to improve the visibility of your page on search engines.
- Use social media to promote your website and improve its visibility on search engines.
Useful tags/attributes
-
no translate attribute
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here.This can be very useful to prevent your brand’s name from being translated to something else.
-
mobile header color meta tag
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here.Now, the background color of the browser will be changed to the one we set, on mobile devices.
Custom HTML element
You can actually create and use your own custom elements in HTML.
-
Declare the element using JavaScript
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here. -
Use it in your HTML
This component was made by Stratis Dermanoutsos. The code can be found here.
Full example:
<body>
<script>
class CustomElement extends HTMLElement {
connectedCallback() {
this.innerHTML = 'This is a custom element.';
}
}
customElements.define('custom-element', CustomElement);
</script>
<custom-element />
</body>
Easy footer example
<footer style="color:rgba(255,255,255,0.3); display:flex; justify-content:space-between; padding:16px;">
©
<script>
document.write(new Date().getFullYear());
</script>
, Stratis Dermanoutsos
</footer>