Project Architectures
MVC
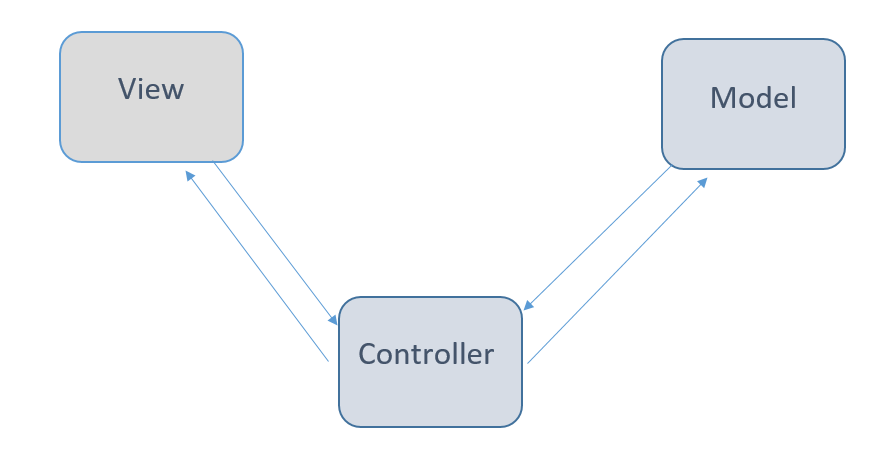
MVC is known as an architectural pattern, which embodies three parts Model, View and Controller. To be more exact it divides the application into three logical parts: the model, the view and the controller.
The three components of MVC
-
Model
It is responsible for maintaining data. The model is actually connected to the database. Adding or retrieving data is done in the model component.
It responds to the controller requests because the controller doesn’t access the database by itself. The model communicates with the database and then gives the needed data to the controller.
The model never communicates with the view directly.
-
View
Data representation is done by the view component. It actually generates UI (User Interface) for the user. So, at web applications think of the view component as the HTML and CSS.
Views are created by the data which is collected by the model component. However, the data itself is not fetched directly from the model component but through the controller.
The view only communicates with the controller.
-
Controller
The controller is the component that enables the interconnection between the view and the model so it acts as an intermediary.
The controller doesn’t have to worry about handling data logic, it just tells the model what to do. After receiving data from the model it processes it and then it sends all that information to the view and explains how to present this data to the user.
views and models cannot communicate directly.
Advantages of MVC
- Components are reusable
- Easy to maintain
- Different components of the MVC application can be independently deployed and maintained
- This architecture helps test components independently
Disadvantages of MVC
- The complexity is high
- Not suitable for small applications
- The inefficiency of data access in view